728x90
증가, 감소 연산자
- 연산자가 항의 앞에 있는 가 뒤에 있는 가에 따라 연산 시점과 결과가 달라진다.
- 문장(statement)의 끝
;을 기준으로 연산결과를 적용한다.
public class OperatorTest {
public static void main(String[] ars) {
int gameScore = 150;
int lastestScore = ++gameScore; // gameScore += 1;
int lastScore = gameScore++;
System.out.println(lastestScore);
System.out.println(lastScore);
System.out.println(gameScore);
}
}
단락 회로 평가(short circuit evaluation)
- 논리 곱
&&: 두 항의 결과가 모두true일 때만true - 논리 합
||: 두 항의 결과가 모두false일 때만false - 비교 대상인 두 항을 봤을 때, 앞의 항만으로도 결과가 예상되면 뒤의 항까지 계산을 하지 않고 결과값을 리턴
public class LogicalTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num1 = 10;
int i = 2;
boolean value = ((num1 = num1 + 10) < 10) && ((i = i + 2) < 10);
System.out.println(value);
System.out.println(num1);
System.out.println(i);
/*
i항의 결과값이 변치 않음 (output : 2)
`&&`를 기준으로 좌측항이 이미 `false`이기 때문에 우측항은 계산 수행 X
*/
}
}
삼항 연산자
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ConditionTest {
public static void main(String[] args){
int max;
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Input1 : ");
int num1 = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("Input2 : ");
int num2 = scanner.nextInt();
max = (num1 > num2) ? num1 : num2;
System.out.println(max);
}
}
비트 연산자
public class bitOperationTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num1 = 5;
int num2 = 10;
System.out.println(num1 | num2);
System.out.println(num1 & num2);
System.out.println(num1 ^ num2);
System.out.println(~num1); //부호도 반전하여 보수로 취한다
System.out.println(num1 << 2); // num1 *= 2^n
System.out.println(num1 <<= 2);
System.out.println(num1 >> 1); // num1 /= 2^n
}
}
연산자 우선순위
- 단항 연산자가 가장 선순위
- 대입 연산자는 가장 후순위
- ⭐ 코드의 가독성을 높이기 위해
괄호를 사용하여 연산 순위를 명확히 표시하는 게 좋다!
조건문
if - else vs if - if
if - else: 하나의 상황에 대한 비교(각 조건은 상호배타적이다.)if - if: 각 다른 조건 문으로 해석되어 각각 수행하게 된다.
switch - case
- 복잡하고 번거로운 부분을 가독성 좋게 구현
import java.util.Scanner;
public class SwitchCaseTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int month = scanner.nextInt();
int day;
switch (month){
case 1: case 3: case 5: case 7: case 8: case 10: case 12:
day = 31;
break;
case 2:
day = 28;
break;
case 4: case 6: case 9: case 11:
day = 30;
break;
default:
System.out.println("존재하지 않는 달입니다.");
day = -1;
}
System.out.println(month + "월은 " +day+ "일까지 존재합니다.");
}
}
Switch Expression
- Java 14부터 지원
yield키워드 사용break사라짐- 리턴 값이 없는 경우는 오류가 생김
- 식과 반환 표현이 가능하다.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class SwitchCaseTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int month = scanner.nextInt();
int day = switch (month){
case 1, 3, 5, 7, 8, 10, 12 ->
31;
case 2->
28;
case 4, 6, 9, 11->
30;
default-> {
System.out.println("존재하지 않는 달입니다.");
yield -1;
}
};
System.out.println(month + "월은 " +day+ "일까지 존재합니다.");
}
}
반복문
- while
- flag 값 체크시에 많이 쓰임
- do-while
- 반복문 이전에 먼저 수행해야할 문장이 있을 경우 쓰임
- for
- for 문의 문장들은 생략 가능(초기화식, 조건식, 증감식)
- 증감식이 복잡할 경우 가독성이 떨어지므로, for문 블럭내에 작성하는 게 좋음
중첩 반복문
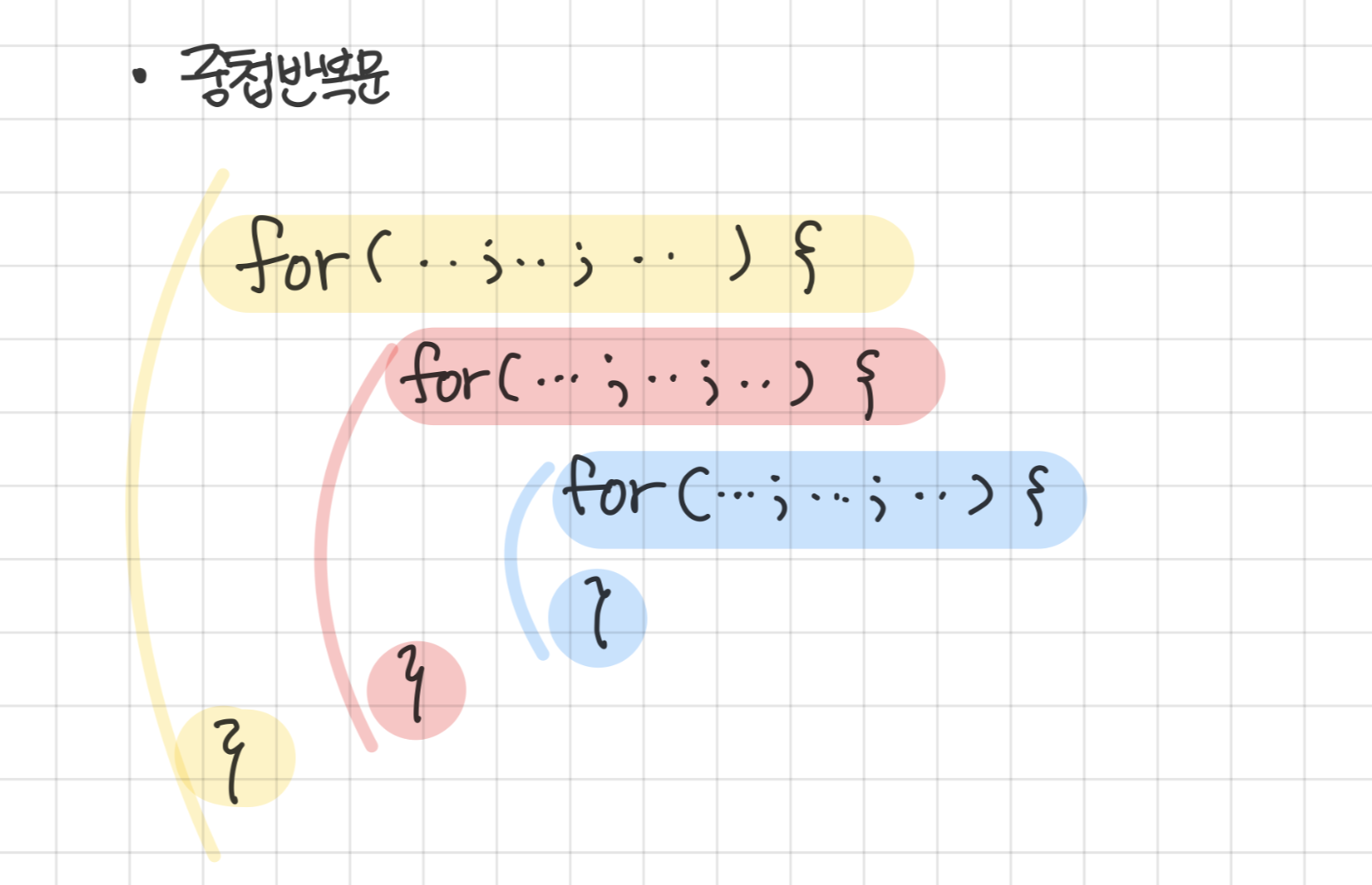
- 반복문 내부에 또 다른 반복문이 있음
- 여러 겹으로 반복문을 겹쳐서 구현 가능 (단 수행시간에 문제가 발생할 수 있음)
- 외부 반복문과 내부 반복문 간의 변수 값 변화에 유의하며 구현
⭐️ 지나친 중첩 반복문은 시간 복잡도를 증가시켜, 프로그램의 성능을 저하시킬 수 있음!
728x90
'🧑💻 Language > Java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Java] 객체 지향 프로그래밍(2) (0) | 2022.04.19 |
|---|---|
| [Java] 객체 지향 프로그래밍 (1) (0) | 2022.04.07 |
| [Java] Basic Java (1) (0) | 2022.03.29 |
| [Java] 멀티스레드 (0) | 2021.10.18 |
| [Java] 14. 스윙 (0) | 2021.06.05 |
