728x90

상속 (inheritance)
: 부모 클래스에 만들어진 필드, 메소드를 자식 클래스가 물려받음
- 상속을 통해 간결한 자식 클래스 작성
- └ 동일한 특성 재정의 필요 ❌ → 자식 클래스의 간결
상속의 장점
- 클래스의 간결화: 멤버의 중복 작성 불필요
- 클래스의 관리 용이: 클래스들의 계층적 분류
- 소프트웨어의 생산성 향상: 재사용과 확장 용이
상속의 특징
- 클래스의 다중 상속 지원 ❌ (클래스를 여러 개 상속 불가)
- 상속 횟수는 무제한이다.
- 상속의 최상위 조상 클래스는 java.lang.Object 클래스이다.
- └ 컴파일러에 의해 자동으로 상속이 이루어진다.
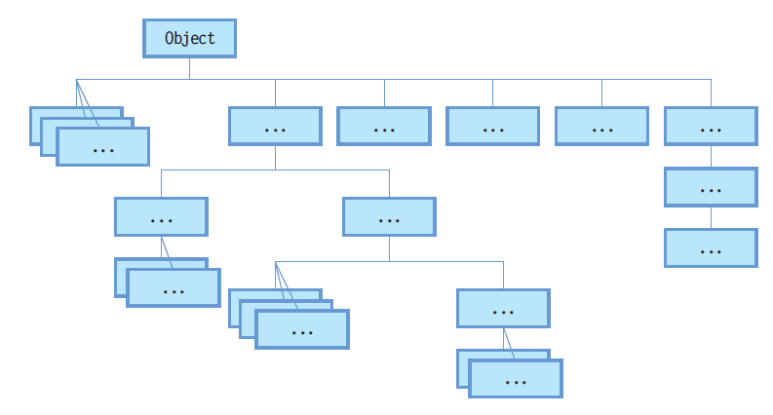
상속 선언
public class Person {
...
}
public class Student extends Person { // Person 을 상속받는 클래스 Student 선언
...
}
public class StudentWorker extends Student { // Student 를 상속받는 StudentWorker 선언
...
}- 부모 클래스 → 슈퍼 클래스(super class) 라고도 함
- 자식 클래스 → 서브 클래스(sub class) 라고도 함
- extends 키워드 사용
- └ 슈퍼 클래스의 확장 개념
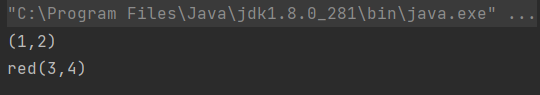
Ex 1
public class ColorPointEx {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Point p = new Point();
p.set(1,2);
p.showPoint();
ColorPoint cp = new ColorPoint();
cp.set(3,4);
cp.setColor("red");
cp.showColorPoint();
}
}
class Point{
private int x, y;
public void set(int x, int y){
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public void showPoint(){
System.out.println("("+x+","+y+")");
}
}
class ColorPoint extends Point {
private String color;
public void setColor(String color){
this.color = color;
}
public void showColorPoint(){
System.out.print(color);
showPoint();
}
}
상속에서의 접근 지정자
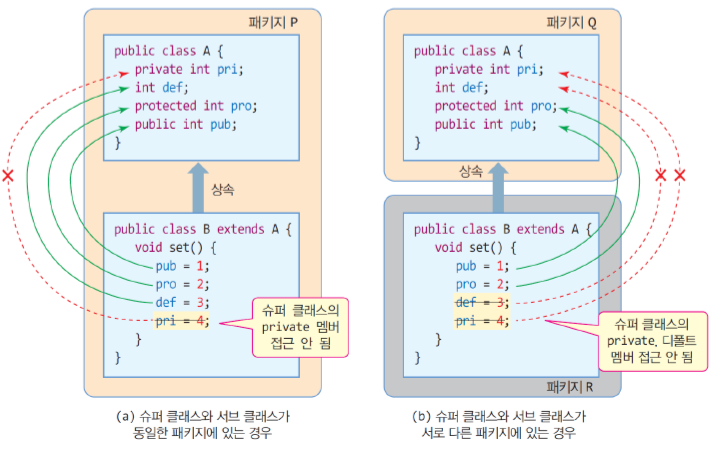
- 슈퍼 클래스내 접근 지정자
- private 멤버 : 동일 클래스 내의 멤버만 허용
- default 멤버 : 패키지 내 모든 클래스 허용
- protected 멤버 : 패키지 내 모든 클래스 허용
- 예외 : 서브 클래스는 다른 패키지에 있어도 접근 허용
- public 멤버 : 다른 모든 클래스 허용
Ex2
class Person {
private int weight;
int age;
protected int height;
public String name;
public void setWeight(int weight) {
this.weight = weight;
}
public int getWeight() {
return weight;
}
}
class Student extends Person {
public void set() {
age = 30;
name = "홍길동";
height = 170;
setWeight(99);
}
}
public class InheritanceEx {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s = new Student();
s.set();
System.out.println(s.age);
System.out.println(s.name);
System.out.println(s.height);
System.out.println(s.getWeight());
}
}
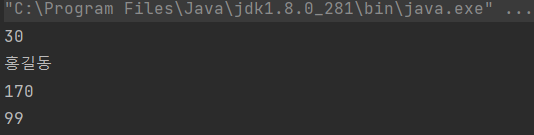
- get메소드, put메소드를 이용해 private 멤버에 간접 접근을 한다.
→ (캡슐화의 특성인 정보 은닉(Information Hiding)')
상속에서의 생성자
new에 의해 서브 클래스의 객체가 생성될 때
- 슈퍼클래스의 생성자와 서브 클래스의 생성자 모두 실행됨
- 호출 순서
- 서브 클래스 생성자 (실행 전) → 슈퍼 클래스 생성자
- 실행 순서
- 슈퍼 클래스 생성자 → 서브 클래스 생성자
- 객체 초기화의 목적성을 둠
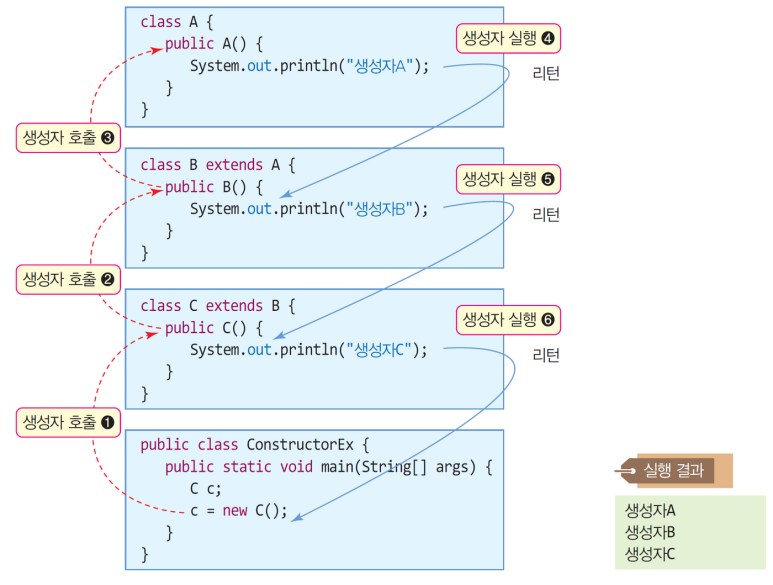
- 슈퍼 클래스와 서브 클래스 둘다 생성자 여러개 작성 가능 (생성자 작성 원칙)
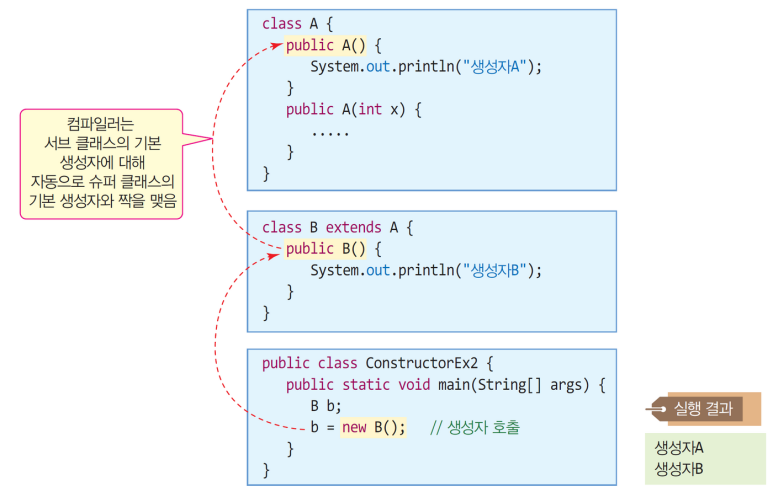
- 서브 클래스 생성자에서 슈퍼 클래스 생성자 하나 선택
└ (생성자 선택 하지 않은 경우, 컴파일러가 자동으로 슈퍼 클래스의 기본 생성자 선택! - super() 함수를 이용해 생성자 호출 가능
- 서브 클래스 생성자 호출 시 슈퍼 클래스 기본 생성자 선택
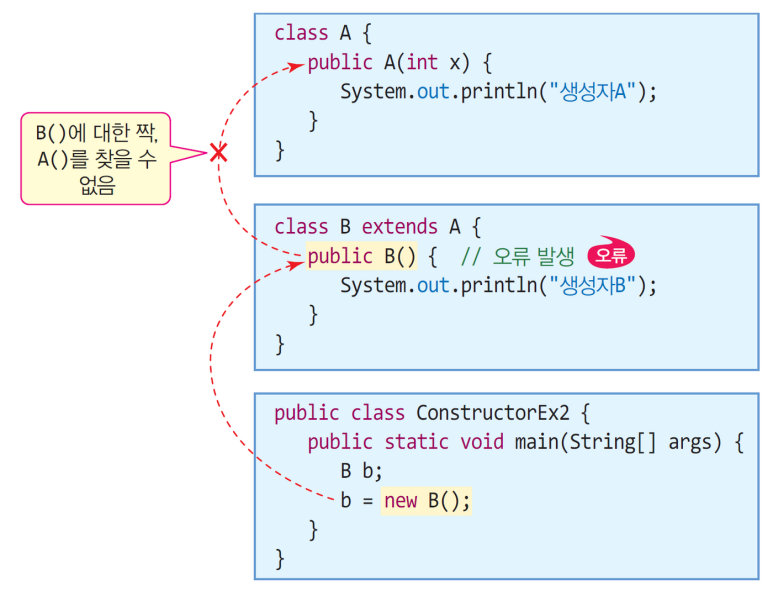
- 슈퍼 클래스에 기본 생성자가 없어, 오류 난 경우
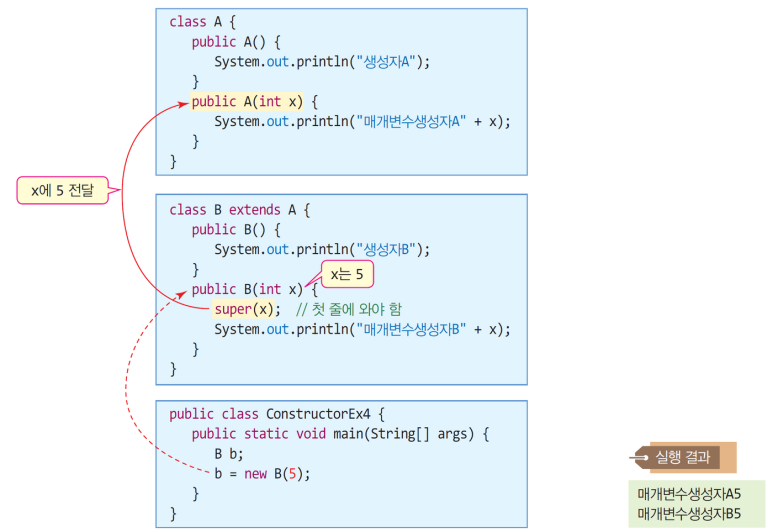
super() 함수를 이용한 명시적 슈퍼 클래스의 생성자 선택
- super(parameter)
- 서브 클래스에서 명시적으로 슈퍼 클래스의 생성자를 선택 호출할 수 있다.
- 생성자를 통해 파라미터 값을 넘겨준다.
- 작성 규칙 : 반드시 서브 클래스 생성자 코드의 제일 첫 줄에 와야한다.
class Point {
private int x, y;
public Point() {
this.x = this.y = 0;
}
public Point(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public void showPoint(){
System.out.println("(" + x + "," + y + ")");
}
}
class ColorPoint extends Point{
private String color;
public ColorPoint(int x, int y, String color) {
super(x, y);
this.color = color;
}
public void showColorPoint() {
System.out.print(color);
showPoint();
}
}
public class SuperEx {
public static void main(String[] args){
ColorPoint cp = new ColorPoint(5, 6, "blue");
cp.showColorPoint();
}
}
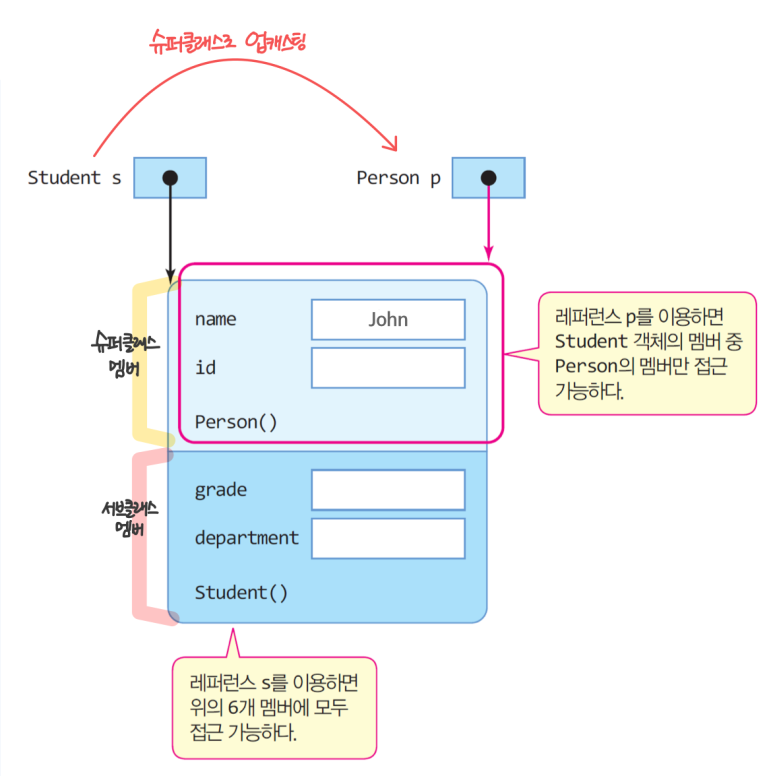
업캐스팅 (upcasting)
- 서브 클래스 객체를 슈퍼 클래스 타입으로 변환
- 업캐스팅된 레퍼런스: 슈퍼 클래스의 멤버만 접근 가능하다. (슈퍼 클래스이므로 서브 클래스의 객체는 접근 불가.)
class Person {...}
class Student extends Person {...}
Student s = new Student();
Person p = s; //업캐스팅(자동 타입 변환 발생)
//객체 p는 슈퍼 클래스의 멤버만 접근 가능Ex3
class Person {
String name;
String id;
public Person(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
class Student extends Person {
String grade;
String department;
public Student(String name){
super(name);
}
}
public class UpcastingEx {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p;
Student s = new Student("John");
p = s;
System.out.println(p.name);
/*
p.grade = "A"; //컴파일 오류
p.department = "Software"; //컴파일 오류
업캐스팅 되어서
서브 클래스의 멤버는 접근 불가
*/
}
}
다운캐스팅(downcasting)
- 슈퍼 클래스 객체를 서브 클래스 타입으로 변환
- 슈퍼 캐스팅과 달리 명시적 타입 변환 필요
class Person {...}
class Student extends Person {...}
...
Person p = new Student("John") //업캐스팅
...
Student s = (Student)p; //다운캐스팅 public class DowncastingEx {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p = new Student("John"); //업캐스팅
Student s;
s = (Student)p; //다운캐스팅
System.out.println(s.name);
s.grade = "A";
}
}
상속
상속 (inheritance)
www.notion.so
아래 노션 페이지에 자바 공부 내용에 대해 업로드 합니다!
수정사항이나 질문사항의 경우 노션 댓글로 남겨주세요!(*•̀ᴗ•́*)و ̑̑
JAVA 이론 정리
주석 단축키 주석 처리하고 싶은 부분을 블록 처리하고 ‘Ctrl+Shift+ / ’를 누르면 /* */로 주석 처리가 됩니다. 주석을 해제하고 싶은 부분을 블록 처리하고 ‘ Ctrl+Shift+ \ (원 표시 혹은 역슬러시)
www.notion.so
개발 환경

작성 플랫폼

728x90
'🧑💻 Language > Java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Java] 9. 추상 메소드와 추상 클래스 (0) | 2021.05.16 |
|---|---|
| [Java] 8. 메소드 오버라이딩 (0) | 2021.05.16 |
| [Java] 6. 메소드 작성과 접근 지정자 (0) | 2021.05.02 |
| [Java] 5. 자바의 객체 지향적 특성 (0) | 2021.05.02 |
| [Java] 4. 배열과 main() 메소드 (0) | 2021.05.02 |
